Navigating the complexities of government assistance programs can be daunting, especially when determining if one benefit impacts another. This guide will delve into the relationship between Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), commonly known as food stamps.
We’ll explore whether SSI counts as income for SNAP eligibility, the potential impact on benefit amounts, and other crucial considerations.
SSI provides financial assistance to individuals with disabilities, the elderly, and blind or disabled children. SNAP, on the other hand, helps low-income households purchase nutritious food. Understanding how these programs interact is essential to maximizing benefits and ensuring food security.
Definition of Supplemental Security Income (SSI)

Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a federal income supplement program funded by general tax revenues (not Social Security taxes) and administered by the Social Security Administration (SSA). SSI provides monthly payments to disabled adults and children, and to people who are blind or over age 65 and have limited income and resources.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for SSI, you must meet the following criteria:
- Be a U.S. citizen or a qualified non-citizen
- Be age 65 or older, blind, or disabled
- Have limited income and resources
Benefit Calculation and Distribution
The amount of SSI benefits you receive is based on your income and resources. The SSA uses a complex formula to calculate your benefit amount. In general, the more income and resources you have, the lower your SSI benefit will be.
SSI benefits are paid in monthly installments. The SSA sends you a check or deposits your benefits directly into your bank account.
Definition of Food Stamps (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program or SNAP)
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as food stamps, is a federally funded program that provides food assistance to low-income individuals and families. SNAP benefits are used to purchase food from authorized retailers.
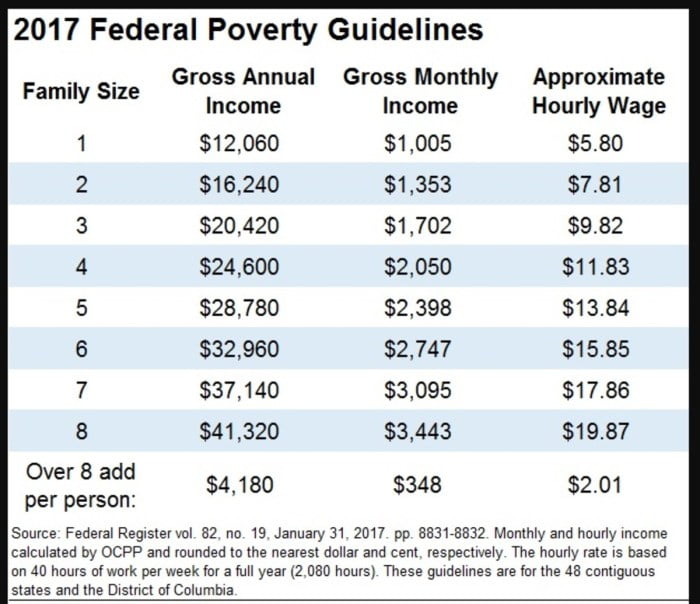
To be eligible for SNAP, individuals and families must meet certain income and asset limits. Income limits vary by state and household size, but generally, households must have a gross income that is below 130% of the federal poverty level.
Asset limits also vary by state, but generally, households cannot have more than $2,500 in countable assets, or $4,000 if one member of the household is disabled or elderly.
How SNAP Benefits Are Calculated and Distributed
SNAP benefits are calculated based on household size and income. The amount of benefits a household receives is determined by a formula that takes into account the household’s income, expenses, and number of eligible members. SNAP benefits are distributed electronically through an Electronic Benefits Transfer (EBT) card.
EBT cards can be used to purchase food from authorized retailers.
Relationship between SSI and SNAP
SSI counts as income when determining SNAP eligibility. However, there are some limitations and restrictions on SSI recipients receiving SNAP benefits.
SSI Income Limits
To qualify for SNAP benefits, SSI recipients must meet specific income limits. The income limits vary depending on the household size and composition. For example, in 2023, the gross income limit for a one-person household is $1,886 per month. For a two-person household, the limit is $2,563 per month.
SSI Resource Limits
In addition to income limits, SSI recipients must also meet certain resource limits to qualify for SNAP benefits. Resources include cash, savings accounts, and other assets. The resource limit for SNAP eligibility is $2,500 for individuals and $3,750 for couples.
Other Restrictions
SSI recipients who receive certain types of income, such as Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), may not be eligible for SNAP benefits. Additionally, SSI recipients who live in institutions or nursing homes may not be eligible for SNAP benefits.
Impact of SSI on SNAP Benefits
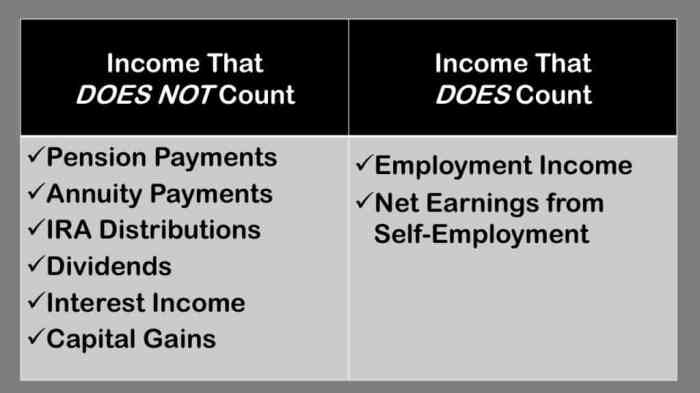
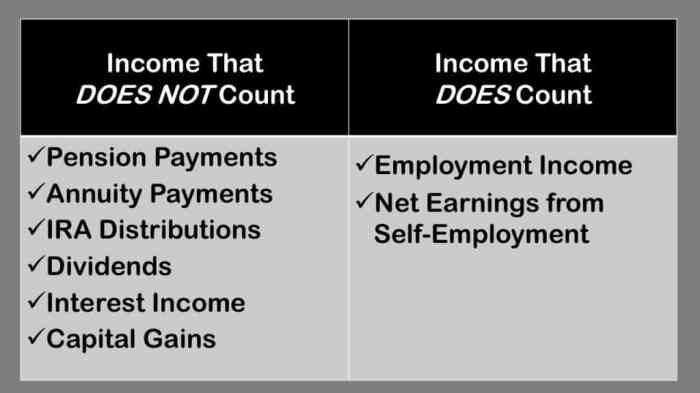
SSI income can affect the amount of SNAP benefits a recipient receives. This is because SSI income is considered countable income for SNAP purposes. Countable income is any income that is counted when determining a household’s eligibility for SNAP benefits and the amount of benefits they receive.The
amount of SSI income that is counted for SNAP purposes depends on the household’s circumstances. For example, if a household has a member who is disabled, the SSI income that the disabled member receives may not be counted as income for SNAP purposes.
However, if a household has a member who is not disabled, the SSI income that the non-disabled member receives will be counted as income for SNAP purposes.
Impact on SNAP Benefit Calculations
The impact of SSI income on SNAP benefit calculations can vary depending on the household’s circumstances. In general, the more SSI income a household has, the lower their SNAP benefits will be. This is because SSI income is counted as income when determining a household’s gross income.
Gross income is the total amount of income that a household has before any deductions are taken. The higher a household’s gross income, the lower their SNAP benefits will be.For example, let’s say that a household has a gross income of $1,000 per month.
If the household has no SSI income, they may be eligible for $200 per month in SNAP benefits. However, if the household has $200 per month in SSI income, their gross income will increase to $1,200 per month. This will result in a decrease in their SNAP benefits, as they may only be eligible for $150 per month in SNAP benefits.
Other Considerations
In addition to the factors mentioned above, there are other considerations that may affect SNAP eligibility for SSI recipients:
Impact of SSI Income on SNAP Benefits
SSI income can affect the amount of SNAP benefits a recipient receives. The SSI income is counted as a gross income when determining SNAP eligibility and benefit amount. However, certain deductions and exclusions may apply, such as:
- Standard deduction
- Earned income deduction
- Dependent care deduction
- Medical expenses deduction
These deductions can reduce the SSI income that is counted for SNAP purposes, thereby increasing the amount of SNAP benefits the recipient may be eligible for.
Potential Changes to SSI and SNAP Policies
Changes to SSI and SNAP policies can also impact the relationship between the two programs. For example, changes to the SSI income limit or SNAP eligibility criteria could affect the number of SSI recipients who are eligible for SNAP benefits.
It’s important for SSI recipients to stay informed about any potential changes to these policies to ensure they continue to receive the benefits they are entitled to.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, while SSI does count as income for SNAP eligibility, it’s crucial to consider individual circumstances and other factors that may affect benefit amounts. By understanding the relationship between these programs, individuals can navigate the complexities of government assistance and access the resources they need to meet their nutritional and financial needs.
FAQ
Does SSI affect the amount of SNAP benefits I receive?
Yes, SSI income is considered when calculating SNAP benefits. The more SSI income you receive, the lower your SNAP benefit amount may be.
Are there any restrictions on SSI recipients receiving SNAP benefits?
Yes, SSI recipients must meet certain eligibility criteria for SNAP, such as income and asset limits. Additionally, SSI recipients may have to provide documentation to verify their disability or blindness.
What other factors can affect SNAP eligibility for SSI recipients?
Other factors that may affect SNAP eligibility for SSI recipients include household size, living arrangements, and any additional income sources.